Select location:
MY


Symptoms of Gum Disease
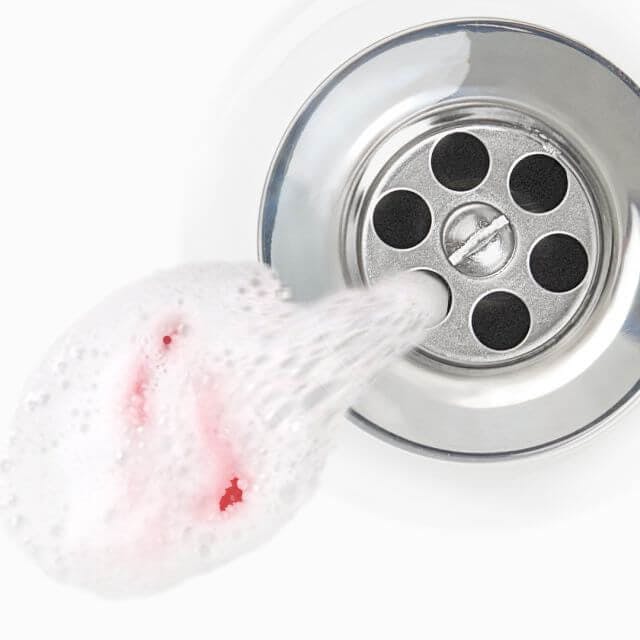
What does it mean when you have bleeding gums?
If your gums bleed when you brush, you may have gum disease and it could lead to bad breath, then inflamed, receding gums and, eventually, even tooth loss.
Whether you see blood in the sink when you brush occasionally or every day, you should never ignore bleeding gums.
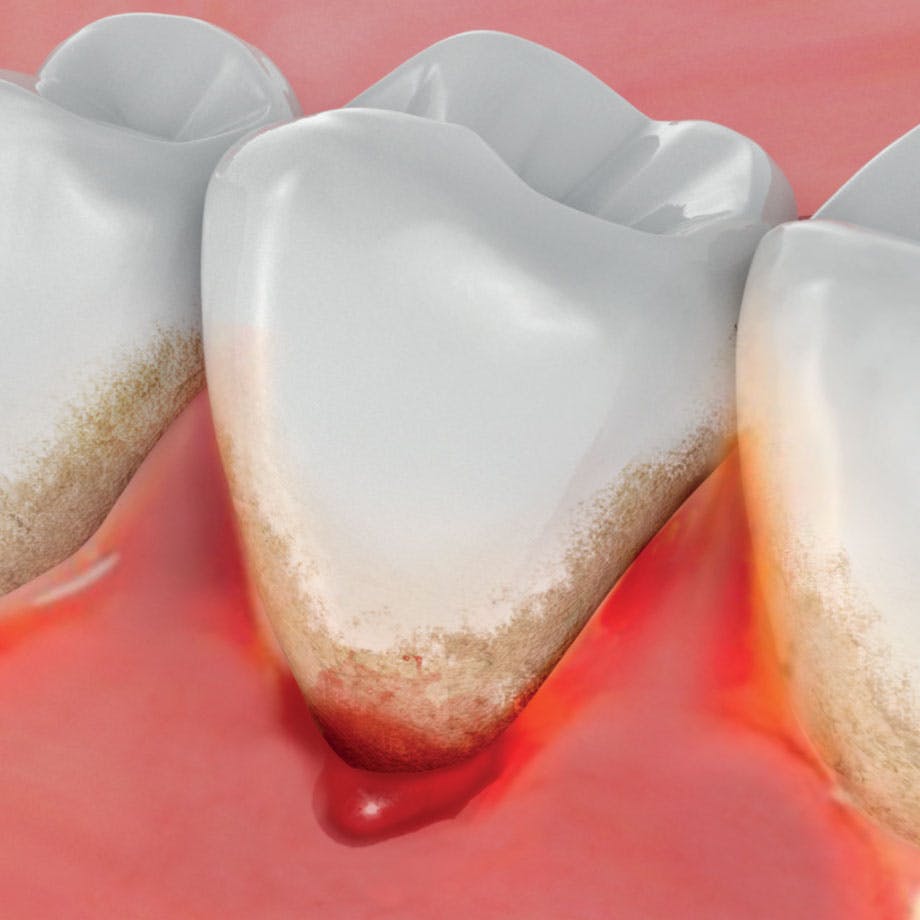
Bleeding gums causes
Bleeding gums tend to be caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that constantly builds up around, on, and in between your teeth. If plaque bacteria is not removed, it can irritate the gums, leading to redness, bleeding and inflammation.
However, there are also a number of other possible causes of gum bleeding. These include over-brushing teeth or brushing too hard,1 a new toothbrush or flossing routine, and some medications.2
How to stop bleeding gums
Regardless of what you think might be the cause of your bleeding gums, the best thing to do is speak to your dentist as soon as possible. They can investigate your symptoms and then advise on the best bleeding gums treatment for you.
There are also a number of simple steps you may wish to consider when it comes to treating bleeding gums – changes to your oral health routine that could help stop the problem becoming more serious. To work effectively, these steps should be followed every day, rather than just on occasions that you notice blood when you spit:
- Brush your teeth twice daily with a toothpaste like parodontax Daily Fluoride Toothpaste. When used twice a day, parodontax daily toothpaste aids plaque removal and helps stop and prevent bleeding gums*.
- Use a manual or electric toothbrush with a small head and soft round bristles, paying particular attention to the gum line.
- Floss or use interdental brushes to remove plaque from hard to reach areas, like in between your teeth.
- Visit your dentist regularly as they may spot problems with your gums before you have any symptoms. If you do experience gums bleeding, report it promptly so your dentist can help you treat it before it becomes more serious
*Consult your dentist for more information about gum problems
1 WebMD. 2016. Gum Problems: Bleeding, Swollen, and Sore Gums. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gum-problem-basics-sore-swollen-and-bleeding-gums. [Accessed 21 June 2016], 2 WebMD. 2016. Gum Problems: Bleeding, Swollen, and Sore Gums. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gum-problem-basics-sore-swollen-and-bleeding-gums?page=2#2. [Accessed 21 June 2016]


